Cars: the future is electric
MTA News – July 2020
For some years now, MTA has been developing and producing components suitable for 48 V electrical architectures to support the most energy-demanding systems.
A dedicated team has identified all possible changes associated with these architectures, creating a range of fuses, fuse holders, power distribution boxes, and connectors.
Download the catalogue
Browse the new "Medium Voltage Solutions" catalogue and discover more.
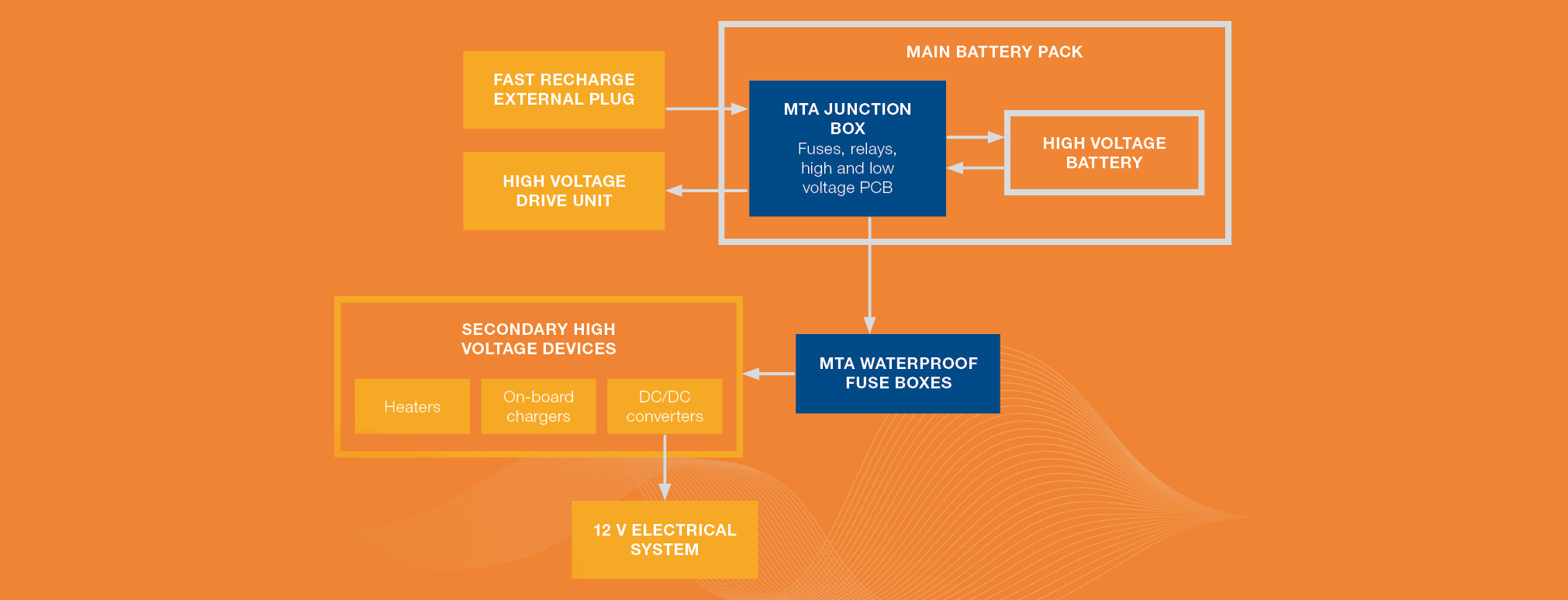
Electric and hybrid cars, which have now become a reality for all car manufacturers, require systems with an increasingly high voltage, so much so that the 48 V is insufficient. Indeed, these vehicles require the management of very high electrical currents and therefore the use of very thick cables with thermal inefficiencies. For this reason, new electrical systems at 400 V or more (up to 850 V), depending on the power of the drive system, must coexist with the traditional 12 V system.
A Research & Development team dedicated to supporting the latest demands of manufacturers for their high voltage systems has upgraded our traditional products, redesigning them according to the new needs of hybrid and battery-powered vehicles. This means we can offer an array of fuse holders, power distribution units and battery junction boxes suitable for high voltage systems. These must necessarily be reliable devices capable of handling enormous amounts of power (tens of constant kilowatts) throughout the vehicle's lifetime and must guarantee users the required levels of safety in all conditions of use due to potentially dangerous voltage levels in the system.
For example, a junction box is a device installed inside the main battery assembly and has the function of cutting the high voltage output of the battery from the vehicle's electrical system when necessary, both for functional and safety reasons. These units operate at a high rated voltage and are sized to provide many tens of kW from the battery pack to the vehicle's electrical system. They contain fuses; relays that can connect/disconnect the main output intended for the vehicle's powertrain system; a section of the high voltage pcb that includes the preload circuit necessary for the drive system's power supply unit; several other control lines to keep the voltage under control at all significant points of the circuit within the unit; a section of the low voltage PCB (12 V) that manages the low voltage signals that control all the internal relays.
Some customers require that the power distribution boxes be waterproof, holding fuses used to supply secondary high voltage devices such as heaters, on-board battery chargers or DC/DC converters.
All high voltage connectors are equipped with the HVIL safety circuit, i.e. a low voltage interlock circuit (12 V) that safely disconnects the high voltage source if any connector is open in order to avoid any risk of electric shock to users or operators.